Nature conservation projects play a pivotal role in safeguarding ecosystems, preserving biodiversity, and fostering sustainable practices across the globe. These initiatives are not just about protecting animals or plants—they’re about creating a healthier planet for future generations. From large-scale wildlife conservation efforts in India to community-driven projects around the world, nature conservation projects offer a pathway toward reversing habitat loss, combating climate change, and ensuring the survival of endangered species. Whether it’s restoring forests, protecting marine life, or promoting eco-tourism, the work done through nature conservation projects has far-reaching implications for both local communities and global environments. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of these projects, exploring their definitions, types, examples, and the challenges they face. By understanding the importance of nature conservation projects, we can better appreciate the delicate balance of our planet and the collective effort required to protect it.
Key Takeaways
- Understand Conservation Projects: Collaborative efforts protecting ecosystems, species, and cultural heritage through organized initiatives.
- Diverse Conservation Types: Engage in ecological, wildlife, habitat restoration, cultural, and urban conservation efforts.
- Prominent Conservation Examples: Support global programs like WWF, UNESCO, and the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority.
- Significant Conservation Benefits: Protect biodiversity, maintain ecosystem services, preserve culture, and ensure long-term sustainability.
- Practical Conservation Actions: Adopt small, impactful strategies like reducing food waste, planting native flowers, and volunteering locally.
- Developmental Conservation Milestones: Recognize the 7 conservation tasks in childhood development, crucial for cognitive growth.

Environmental Conservation Projects
Environmental conservation refers to efforts aimed at protecting, restoring, and managing ecosystems to maintain biodiversity, sustain natural resources, and promote environmental health. These projects often involve a combination of ecological restoration, habitat preservation, and sustainable practices to address the impacts of human activities on the planet.
- Reforestation and Afforestation: Planting trees in degraded areas to restore forest ecosystems and prevent desertification. This helps in combating deforestation and improving air quality.
- Wetland Restoration: Initiatives focused on revitalizing wetlands to enhance biodiversity and improve water purification capabilities, preventing nutrient runoff and pollution.
- Coastal Zone Protection: Projects aimed at safeguarding beaches, mangrove forests, and coral reefs through measures like artificial reef construction and buffer zone establishment.
- Biodiversity Enhancement: Efforts to restore habitats for endangered species and promote genetic diversity among populations through targeted conservation actions.
- Pollution Control and Clean-Up: Programs focused on reducing water, soil, and air pollution through waste management systems, treatment plants, and community-driven clean-up initiatives.
- Carbon Sink Development: Planting trees and mangroves to act as carbon sinks, aiding in carbon sequestration and mitigating climate change impacts.
- Sustainable Agriculture and Forestry Practices: Implementing eco-friendly farming techniques, agroforestry, and organic farming to reduce environmental degradation associated with conventional methods.
- Urban Green Spaces Creation: Developing green infrastructure in cities, such as green roofs, vertical gardens, and parks, to improve air quality and support local biodiversity.
- Community-Based Conservation Education: Running awareness campaigns and training programs to educate communities on environmental stewardship and sustainable practices.
- Ecotourism and Sustainable Travel: Promoting responsible tourism that supports conservation efforts, such as eco-certified accommodations and guided nature tours that contribute to local conservation goals.
Nature Conservation Examples
- The establishment and protection of national parks around the world, such as Yellowstone National Park in the United States and the Amazon Rainforest in Brazil.
- Creation of wildlife refuges and preserves, including the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park in Australia and the Serengeti in Tanzania.
- Implementation of protected species programs , like the Golden Lion Tamarin Project in Brazil and the California Condor Recovery Program in the United States.
- Support for community-based conservation initiatives, such as the Maasai Mara in Kenya and the Gorongosa National Park in Mozambique.
- Development of urban green spaces and eco-tourism projects, including Central Park in New York City and the Singapore Botanic Gardens.

Example of a Conservation Project
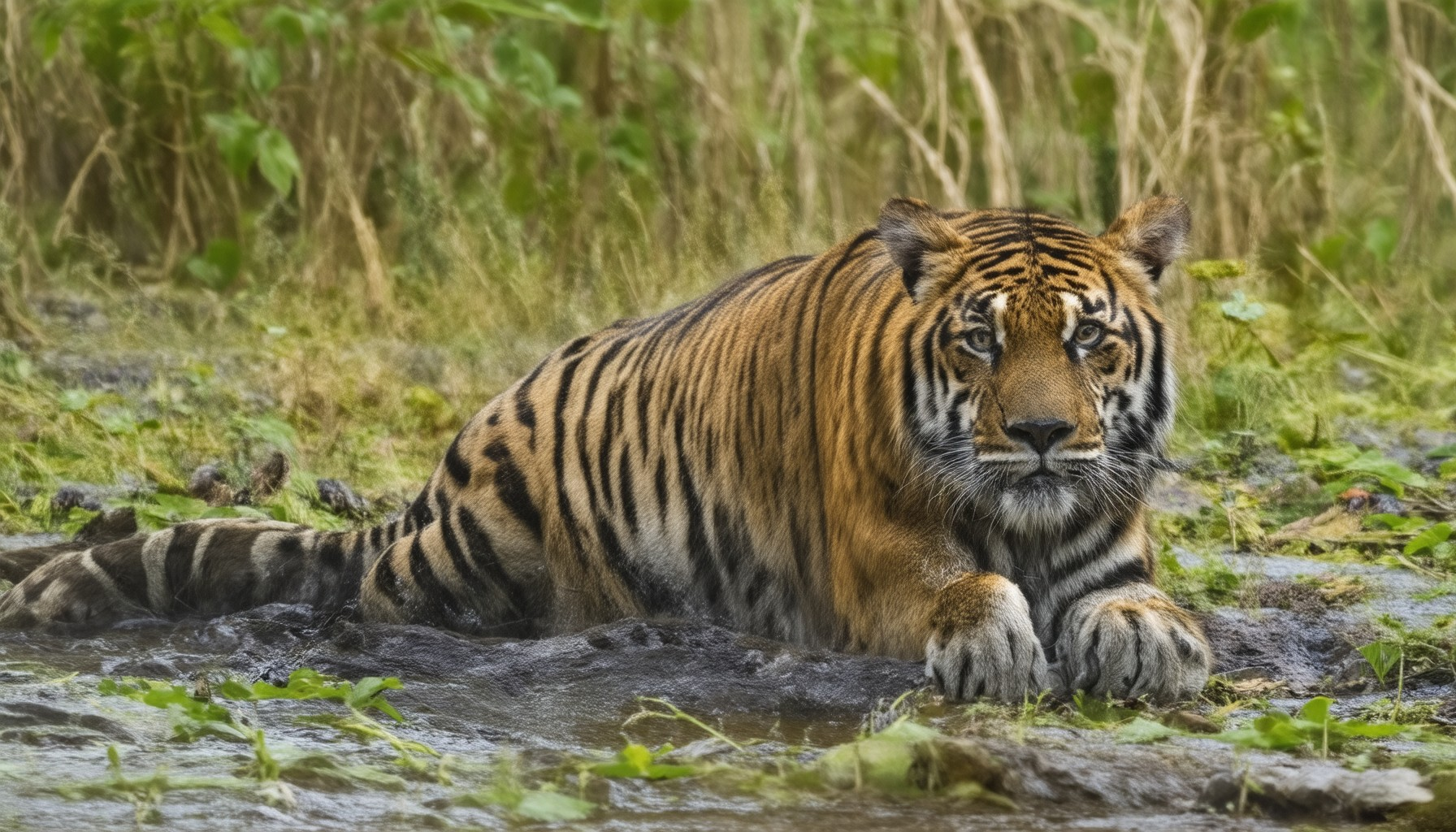
The restoration of the Greater One-Horned Rhinoceros population in Manas National Park, Assam, India, is a remarkable example of a successful conservation project. Once extinct in the region due to decades of poaching, habitat loss, and civil unrest, this initiative has brought the species back from the brink.
Initiated in the early 1990s, the project aimed to restore the rhino population in the UNESCO World Heritage Site. Through collaborative efforts involving governments, NGOs, and local communities, the program has achieved significant milestones:
- Reintroduction of 30+ rhinos into the park
- Expansion of the park’s boundaries to safeguard habitats
- Establishment of anti-poaching units and surveillance systems
- Educational programs for local communities to reduce human-wildlife conflicts
The success of this project is attributed to its holistic approach, combining wildlife protection with ecosystem restoration and community engagement. This serves as a model for other conservation efforts worldwide, demonstrating the importance of collaboration and sustained commitment to protecting endangered species and their habitats.
Inxchan supports various wildlife conservation initiatives around the globe, offering opportunities for individuals to volunteer and contribute to these important causes. Learn more about our efforts and how you can get involved by visiting our wildlife conservation page.

What Are Conservation Projects?
Conservation projects refer to organized efforts aimed at protecting, restoring, and managing ecosystems, species, and cultural heritage to ensure their survival and prosperity. These initiatives can take various forms, ranging from environmental preservation to cultural preservation, and often involve collaboration between governments, NGOs, local communities, and international organizations.
Types of Conservation Projects
- Ecological Conservation
- Wildlife Conservation : Programs focused on protecting endangered species and their habitats.
- Habitat Restoration : Efforts to rebuild degraded ecosystems, such as forests, wetlands, and grasslands.
- Pollination Initiatives : Projects aimed at supporting pollinator species, crucial for ecosystem health.
- Cultural Conservation
- Heritage Preservation : Efforts to protect historical sites, artifacts, and cultural practices from disappearing.
- Language Revival : Programs dedicated to reviving endangered languages and preserving linguistic diversity.
- Cultural Landscapes : Projects involving the protection and restoration of culturally significant landscapes.
- Urban Conservation
- Green Space Creation : Initiatives to establish parks, gardens, and green infrastructure within cities.
- Sustainable Urban Development : Efforts to integrate eco-friendly practices into urban planning and construction.
Examples of Conservation Projects
- WWF Global Conservation Program : A leading initiative focused on protecting wildlife and ecosystems worldwide.
- UNESCO World Heritage Site Preservation : Efforts to safeguard globally significant cultural and natural sites.
- The Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority : A program managing the health and sustainability of the Great Barrier Reef.
Importance and Benefits
- Biodiversity Protection : Ensures the survival of diverse species and ecosystems.
- Ecosystem Services : Maintains processes like water purification and climate regulation.
- Cultural Significance : Preserves humanity’s history, traditions, and shared knowledge.
- Sustainability : Contributes to long-term environmental stability and human well-being.
By addressing these areas, conservation projects play a vital role in fostering a healthier planet and a richer cultural legacy for future generations.
What Are the 7 Conservation Tasks?
The 7 conservation tasks, as outlined by Jean Piaget, are essential milestones in a child’s cognitive development. These tasks help children understand the world around them and form the basis of their problem-solving abilities. Below is a breakdown of each task:
- Number Conservation : Children begin to recognize quantities and understand the concept of numbers. They learn to count objects and understand relationships between numbers. This skill typically emerges around age 6.
- Length Conservation : Children start to measure objects and recognize differences in length. They understand that two objects with the same length are equal, even if they look different. This skill develops around age 6.
- Liquid Conservation : Children grasp the concept of quantity in liquids. They learn that two containers with the same amount of liquid, even if shaped differently, are equal. This skill usually appears around age 7.
- Mass Conservation : Children understand that different objects can have the same mass. They learn that two objects with the same mass are equal, regardless of their shape or size. This skill typically emerges around age 8.
- Area Conservation : Children realize that two shapes can cover the same area, even if they look different. They understand that area is independent of shape. This skill develops around age 9.
- Weight Conservation : Children learn that two objects can have the same weight, even if they look different. They understand that weight is independent of shape or size. This skill typically appears around age 9.
- Volume Conservation : Finally, children grasp that two objects can have the same volume, even if they look different. They understand that volume is independent of shape or size. This skill is usually mastered by age 10.
These tasks are crucial in a child’s development and are often used to assess cognitive abilities. Understanding these tasks can help parents track their child’s progress and support their learning journey.
Explore more about child development and learning with our comprehensive guide on Piaget’s Conservation Tasks and how they relate to travel and volunteer opportunities .

Small Conservation Ideas
Conservation doesn’t always require big actions. Here are some simple ways you can make a difference:
- Reduce Food Waste: Buy only what you need, store leftovers properly, and compost organic scraps. This helps conserve resources and reduces landfill waste.
- Plant Native Flowers: Choose plants suited to your region to support local ecosystems and attract pollinators like bees and butterflies.
- Turn Off Lights When Not Needed: Energy conservation starts at home. Unplug devices when not in use and use LED bulbs for lower energy consumption.
- Support Local Conservation Efforts: Volunteer for clean-up drives or join community initiatives focused on environmental protection. Your local efforts can have a lasting impact.
- Minimize Fertilizer Use: Over-fertilizing can harm water quality. Use eco-friendly alternatives and apply fertilizers sparingly to prevent excessive growth.
- Get Involved in Tree Planting: Join reforestation projects or local tree-planting events to help restore forests and combat deforestation.
- Use Reusable Products: Reduce plastic waste by choosing reusable containers, water bottles, and bags. Small changes can add up quickly!
- Adopt a Pet Fish: Consider adopting a fish from a local aquarium shop to reduce the demand for wild-caught fish and help marine conservation efforts.
- Volunteer for Beach Cleanups: Help remove debris from coastal areas to protect marine life and keep our beaches clean for everyone.
- Participate in Birdwatching Events: By monitoring bird populations, you can help identify threats and support conservation efforts for these vital species.
- Reduce Water Usage: Install low-flow fixtures and fix leaks to save water and protect local water sources.
- Join a Community Garden: Grow your own fruits, vegetables, and herbs to promote sustainable living and reduce your carbon footprint.
- Support Dark Sky Initiatives: Reduce light pollution by using dark-sky friendly lighting and joining campaigns to protect night skies.
- Recycle and Repurpose Materials: Turn unwanted items into new products or donate them to local organizations that can reuse them effectively.
- Spread Awareness: Share conservation messages with friends and family to encourage others to take action. Knowledge spreads quickly, and so does positive change!
Conclusion: Every small action counts toward a larger goal. By making mindful choices in your daily life, you can contribute to meaningful conservation efforts and create a healthier planet for future generations.




0 Comments